What is Entra ID?
Entra ID (formerly Azure Active Directory) is a cloud-based identity and access management service that allows organizations to secure and manage user identities and access to applications and resources. As more enterprises move to the cloud, Entra ID has become an essential security infrastructure component. Entra ID Privileged Identity Management (PIM) is a feature of Entra ID that helps organizations manage and secure privileged identities. It provides just-in-time access and access reviews to privileged roles, reducing the risk of privilege abuse.
Authentication context is another feature of Entra ID that enhances security by providing additional context around access requests, such as user location and device information. Entra ID PIM and authentication context provide a robust security solution for managing privileged identities and securing access to critical resources.
What is Privileged Identity Management (PIM)?
Privileged accounts are user accounts or service principals that have extensive access to critical resources and systems in an organization. Attackers often target these accounts since gaining access to them can lead to a complete compromise of the organization’s security. Entra ID Privileged Identity Management allows organizations to manage these privileged accounts, reducing the risk of abuse and unauthorized access.
Entra ID PIM allows organizations to set up just-in-time access and access reviews for privileged roles, ensuring that users only have access to privileged roles when they need it for a limited time. This reduces the risk of privilege abuse and limits the impact of any potential security breaches. Entra ID PIM also allows organizations to monitor privileged access, view audit logs, and generate reports, providing a comprehensive view of privileged identity usage across the organization. Implementing Entra ID PIM is essential for organizations that want to securely and effectively manage their privileged identities.
Conditional Access Authentication Context in Entra ID
Conditional Access Authentication Context is an essential feature of Entra ID that helps organizations secure access to critical resources. Authentication context provides additional information about a user’s access request, such as device information, location, and network details. This additional context can help organizations make more informed access decisions and improve their security posture. Entra ID supports several authentication context features, including device-based conditional access policies, risk-based conditional access policies, and IP-based restrictions. These features allow organizations to customize their authentication policies based on their specific security requirements, making it easier to balance security and productivity.
Conditional Access Authentication Context is not only for Privileged Identity Management. Organizations can configure session policies to enforce stronger requirements for access. Based on the data and context, administrators can apply granular control over access to Cloud apps, including Office 365, based on the user’s compliance status and device type.
Sensitivity labels in SharePoint can also be applied to resources to ensure only authorized users can access them. Through Conditional Access you can configure Sign-in frequency to further enhance security measures.
How Entra ID Privileged Identity Management and Authentication Context Work Together
Entra ID Privileged Identity Management and authentication context are complementary features that can be used together to provide robust security for privileged identities. When a user requests access to a privileged role, the authentication context is used to determine if the user meets all the requirements to access the requested role. By leveraging authentication context, organizations can customize their access policies based on specific security requirements, making it easier to balance security and productivity.
Entra ID Authentication Strengths
Authentication strength is a powerful feature in Entra ID that allows administrators to control which combination of authentication methods can access a resource. For example, they can make only the most secure, phishing-resistant authentication methods available to access sensitive resources while allowing less secure multifactor authentication combinations, such as password + SMS, to access non-sensitive resources.
This level of control is made possible by the Authentication methods policy, which administrators can use to define which authentication methods are available for specific users and groups across Entra ID federated applications. With authentication strength, administrators can go even further by restricting the usage of these methods based on specific scenarios, such as sensitive resource access, user risk, location, and more.
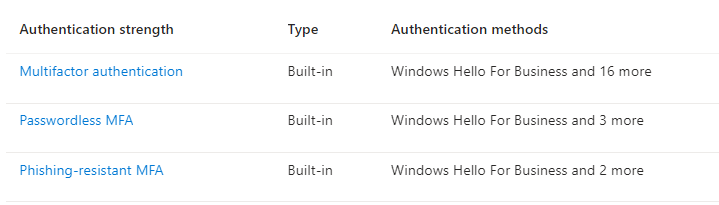
Administrators can create a Conditional Access policy with the “Require authentication strength” control to specify an authentication strength for accessing a resource. Entra ID offers three built-in authentication strengths to choose from:
- Multifactor authentication strength
- Passwordless MFA strength
- Phishing-resistant MFA strength
Alternatively, administrators can create a custom authentication strength based on the authentication method combinations they want to allow.
By leveraging authentication strength in Entra ID, organizations can ensure that the appropriate level of security is applied to different resources based on their sensitivity and risk associated with their access. This can help reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches and improve the organization’s overall security posture.
How to configure Entra ID Privileged Identity Management and Authentication Context
Securing administrative accounts has become increasingly important in today’s digital age, as these accounts grant significant privileges and access to sensitive data. One way to enhance security is through step-up authentication, which requires users to provide additional authentication beyond their initial login credentials in certain situations. An example of step-up authentication is the requirement for a FIDO2 Security Key to activate the Entra ID Global Administrator role.
This role grants significant privileges and access to sensitive data, so requiring a FIDO2 Security Key adds an extra layer of security to prevent unauthorized access. For example, a test user may have the authenticator application configured but no FIDO2 security key attached to their account. This user would be required to provide additional authentication beyond their initial login credentials in order to access sensitive data or perform important administrative tasks. These measures can help businesses and individuals protect their sensitive data and maintain a secure online presence.
Requirements
- Entra ID Global Administrator Permissions
- Test user account without the FIDO2 Security Key
- Eligible for Entra ID Global Administrator Role
- Multi-factor Authentication enabled
- Entra P2 licenses
Configure Authentication Context
- Log in to the Azure portal (porta.azure.com) and navigate to the Entra ID
- Select Security
- Select Conditional Access
- From the Conditional Access page, choose Authentication Context
- On the Authentication Context page, choose + New Authentication Context
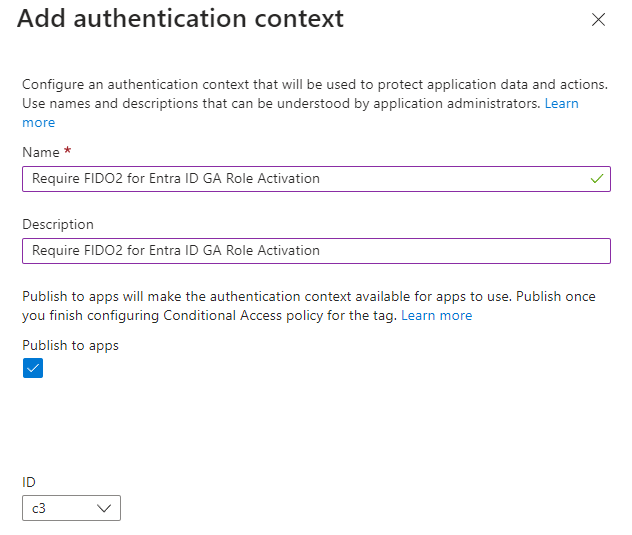
- On the Add authentication context window, fill out the following information:
a. Name: Require FIDO2 for Entra ID GA Role Activation
b. Description: Require FIDO2 for Entra ID GA Role Activation
Configure Entra ID Role Privileged Identity Management settings
- Log in to the Azure portal (porta.azure.com) and search for Privileged Identity Management
- On the Privileged Identity Management page, choose Entra ID Roles
- Select Roles under the Manage
- Open Entra ID Global Administrator role settings
- On the Global Administrator page, choose Settings
- On the Role setting details – Global Administrator page, choose Edit
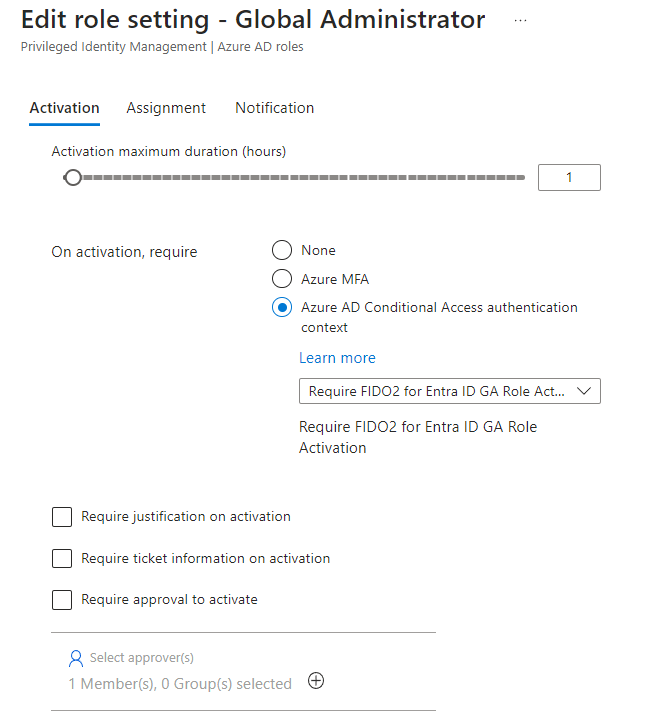
- On the Edit role setting – Global Administrator page, enable the On activation, require Entra ID Conditional Access authentication context setting, and choose the Require FIDO2 for Entra ID GA Role Activation authentication context.
- Click Update
Create Conditional Access Rule
- Log in to the Azure portal (porta.azure.com) and navigate to the Entra ID
- Select Security
- Select Conditional Access
- Click the “+ New Policy” button to create a new policy.
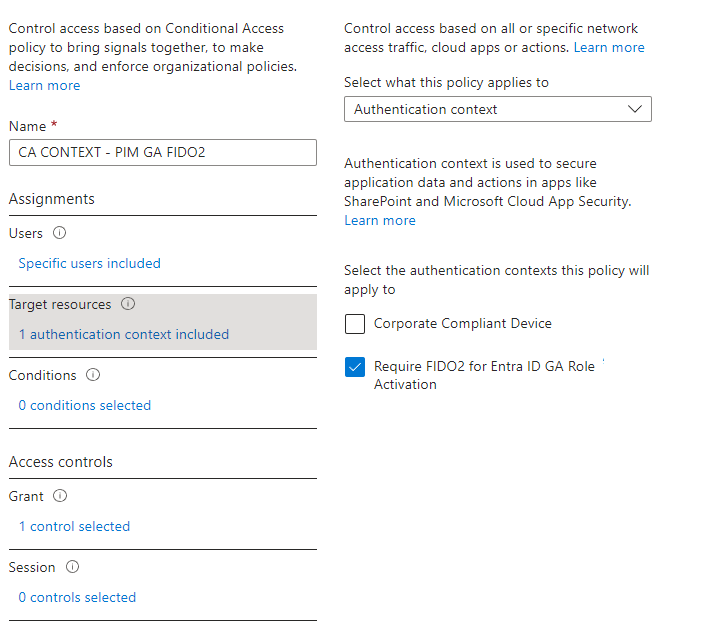
- Give your policy a name
a. Name: CA CONTEXT – PIM GA FIDO2 - Select Users
a. You can select all users, specific users, or groups or exclude specific users or groups. - Select Cloud apps or actions
a. Set the Select what this policy applies to Authentication Context
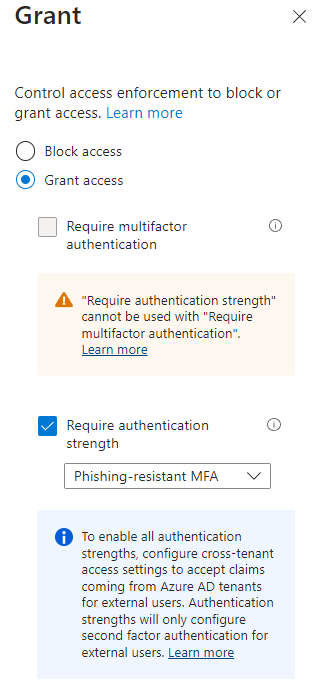
b. Select Require FIDO2 for Entra ID GA Role Activation authentication context - Select Grant
a. Enable the Require Authentication Strength policy and choose Phishing-resistant MFA - Set the policy status to On
- Click “Create” to save your policy
Testing
- Open your test VM and login into the Azure portal (porta.azure.com)
a. Use a test user where you don’t have the FIDO2 Security Key configured. - Open the Privileged Identity Management page
- On the Privileged Identity Management page, choose My Roles
- Under the Entra ID Roles, you should see Global Administrator Role
- Click Activate
- On the Activate – Global Administrator window, you should see the following message “A Conditional Access policy is enabled and may require additional verification. Click to continue.”
- Click on the message, and you should see the following message
- In this case, you see the above message because we didn’t use the FIDO2 security key, and for that test user, it is not configured as well.
- From the Entra ID Sign-in logs, we can see that the user didn’t meet the requirements
Summary
By using Entra ID Privileged Identity Management and Authentication Context, organizations can effectively manage their privileged identities and reduce the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive resources. With the ability to configure authentication context, administrators can ensure that the appropriate authentication methods are used for accessing resources based on the resource’s sensitivity and the risk associated with the user. Additionally, by using Conditional Access policies, administrators can further control access to resources by requiring specific authentication methods or applying additional access controls based on specific conditions. With these tools at their disposal, organizations can effectively secure their resources and prevent unauthorized access while still allowing their users to be productive and efficient.